Which Type of Nitrogen is Greatest for Crops
Nitrogen is likely one of the most essential vitamins for vegetation as a result of it’s nearly all the time briefly provide. The quantity of nitrogen obtainable controls plant development.
Artificial fertilizer often provides nitrogen as urea or nitrate. Natural fertilizer provides it as proteins and amino acids, they usually declare these types are higher for vegetation. Which types of nitrogen can vegetation use, and which is the perfect kind for gardeners to make use of for rising vegetation?
Key Takeaways
- Nitrate and ammonium are the primary types of nitrogen utilized by vegetation.
- Crops can use urea and amino acids instantly.
- Crops additionally appear to have the ability to digest proteins after which soak up them by way of roots, most likely as amino acids.
- Natural gardening strategies don’t appear to considerably alter the amino acids in soil.
Totally different Types of Nitrogen
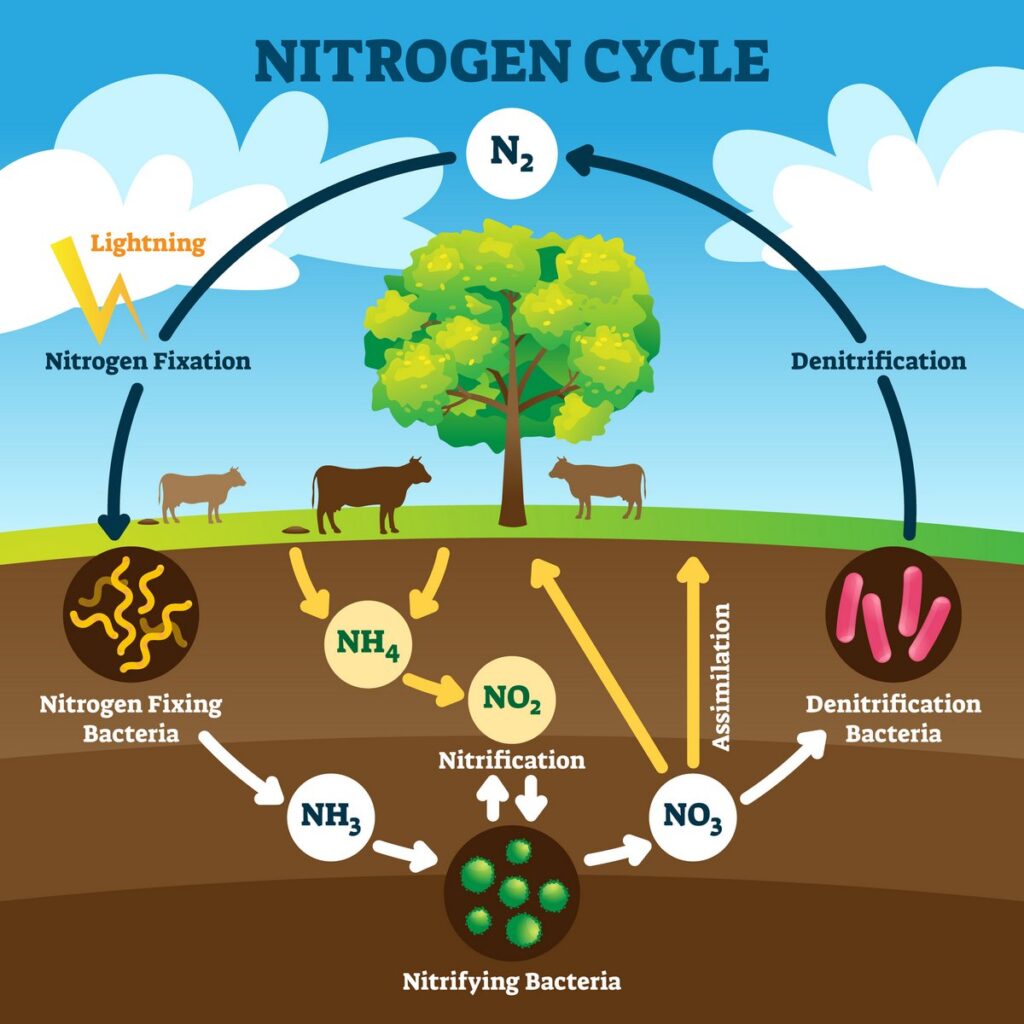
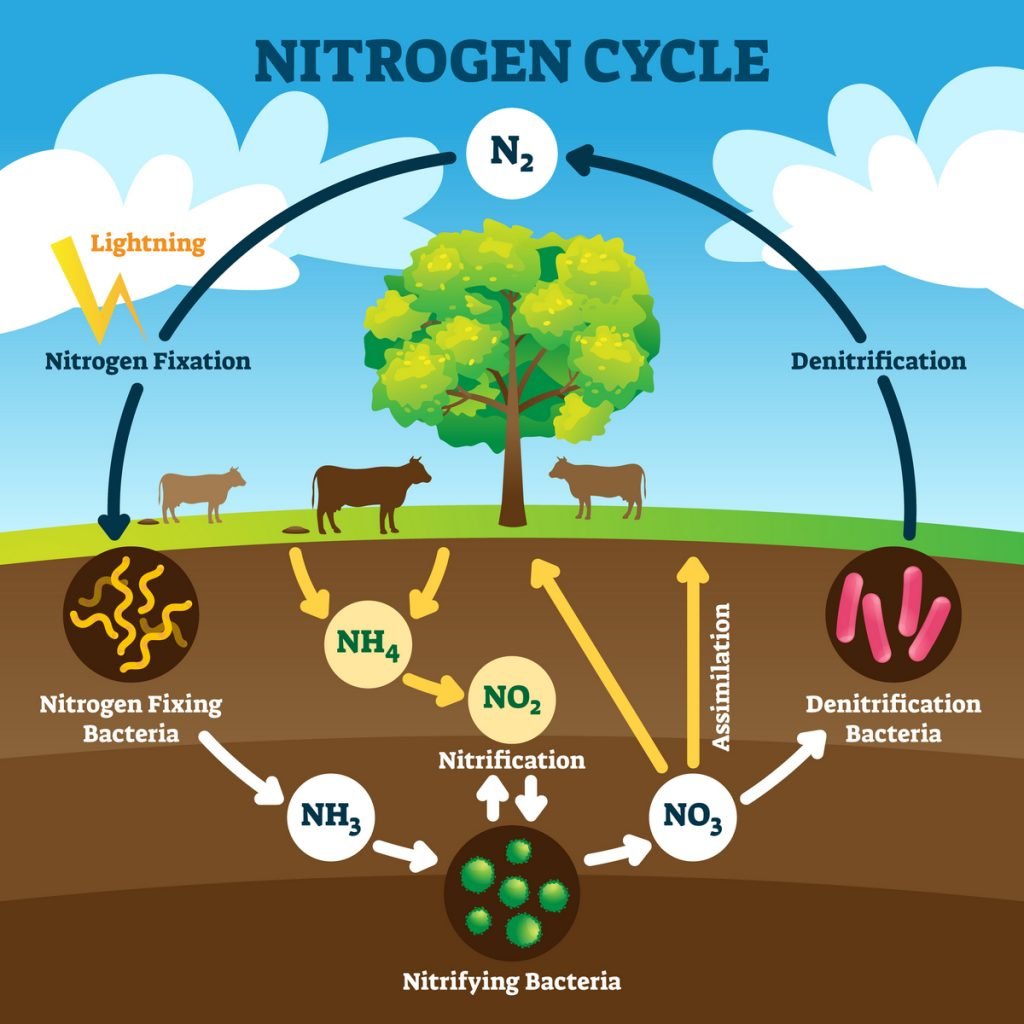
Nitrogen is accessible in lots of types, however just some types can be utilized by vegetation. The commonest kind is N2, which makes up 78% of the air we breathe. However vegetation can’t use this type of nitrogen.
You may need heard that some vegetation, like legumes, can “repair” nitrogen from the air, however that may be a fantasy. Solely micro organism and another microbes can do this. Legumes make the most of rhizobium micro organism to repair nitrogen for his or her use.
Inorganic types of nitrogen embrace ammonium (NH₄⁺), nitrite (NO₂⁻), and nitrate (NO₃⁻). Crops can soak up ammonium and nitrate by way of their roots. These types of nitrogen, in addition to urea, are simply transformed from one to a different by micro organism within the soil.
Urea (CO(NH₂)₂) is essentially the most generally manufactured type of nitrogen as a result of it’s comparatively cheap to make. Chemists contemplate it to be natural as a result of it incorporates carbon. Natural gardeners contemplate it to be artificial as a result of it’s manufactured. Urea can also be produced naturally throughout the decomposition of natural materials, and vegetation produce it internally as a part of their metabolism.
Nitrogen can also be present in every kind of huge molecules, together with amino acids, proteins, DNA, RNA, and chlorophyll. Protein incorporates 16% nitrogen.
Crops Use Nitrate and Ammonium
The first supply of nitrogen for vegetation is nitrate and ammonium. Each types are present in fertilizer.
Nitrate is very soluble and cellular in soil, making it available to plant roots. It strikes with water by way of the soil profile. Most vegetation have specialised nitrate transporters that actively soak up it into roots.
Ammonium, however, is much less cellular as a result of it binds to negatively charged soil particles. Crops have separate ammonium transporters and may rapidly soak up it by way of roots.
In most cardio (well-aerated), impartial to barely alkaline soils, nitrate is the dominant kind of nitrogen absorbed, accounting for 70% of the nitrogen absorbed. It’s because it’s extra cellular and extra secure in oxygen-rich soils. Additionally, many vegetation present a greater affinity for nitrate, significantly throughout lively development.
In distinction, ammonium turns into extra important in acidic and waterlogged soil, the place it’s extra secure than nitrate.
Some plant species, corresponding to tea, rice, and blueberries, want ammonium-dominated diet, whereas corn, wheat, and lettuce are likely to favor nitrate. For a lot of crops, optimum development is achieved with a nitrate to ammonium ratio between 2:1 and 4:1.
Can Crops Use Urea?
Sure, plant roots can soak up urea instantly, however that is not the first means vegetation take up nitrogen.
Urea (CO(NH₂)₂) is a small, uncharged molecule that may go by way of cell membranes, and a few vegetation do have urea transporters of their root cells to assist soak up it. Nevertheless, direct uptake of urea by roots happens solely in small quantities in comparison with nitrate and ammonium.
Crops can soak up urea by way of leaves after a foliar spray. It’s also fashioned inside plant cells as a standard metabolic course of. When correctly utilized, urea produces the identical crop yields as different types of nitrogen.
Urea will not be very secure in soil as a result of microbes convert it to ammonium in 1-3 days. They then convert it to nitrate over a 1-3 week interval. The quantity of urea in soil is generally fairly low.
So whereas urea will be absorbed instantly, a lot of the nitrogen from urea enters the plant as ammonium or nitrate after it’s remodeled within the soil.
Can Crops Use Amino Acids?
Amino acids are a gaggle of about 20 small natural molecules that serve because the constructing blocks of proteins. A lot of the amino acids in soil come from decomposing plant and animal materials.
Crops have particular transporters in root cell membranes that may take up free amino acids instantly from the soil answer. This course of is named natural nitrogen uptake. As soon as inside the foundation, amino acids can be utilized instantly in metabolism, saving the plant the power wanted to make them.
In some pure ecosystems, particularly in chilly, acidic, or organic-rich soils, like boreal forests or tundra, amino acid uptake will be substantial, typically as much as 30–80% of complete nitrogen uptake.
Nevertheless, in agricultural soils and most backyard soils, amino acid uptake is often lower than 5% of complete nitrogen absorbed. It’s because:
- Microbial exercise is excessive, which decomposes amino acids rapidly into ammonium and nitrate. Their half-life in topsoil at 18°C is 2 hours, with a spread of 1–12 hours relying on soil kind and environmental situations.
- Fertilizers provide inorganic nitrogen.
Crops can use amino acids as a nitrogen supply, however since regular ranges are low in gardening soil, they don’t usually play a major position in offering vegetation with nitrogen.
Do Amino Acids in Fertilizer Have an effect on Plant Progress
Crops can soak up amino acids, however not as successfully as nitrate or ammonium. It has been claimed by gardeners that fertilizer containing amino acids will develop higher vegetation. Is that true?
A research on tomato vegetation discovered that including amino acids to common inorganic fertilizer didn’t enhance plant development, but it surely did result in the next content material of some minerals in leaves.
Utilizing amino acids as a foliar spray did enhance the expansion and fruiting of peach bushes. The controls have been unsprayed bushes, however it isn’t clear if the controls had ample entry to nitrogen within the soil.
Do Natural Strategies Improve the Amino Acid Stage in Soil?
It could appear logical that natural strategies that use issues like manure and compost would improve the amino acid stage in soils, in comparison with the usage of artificial fertilizer.
A research that checked out this discovered that natural and traditional soils didn’t considerably differ of their soil amino acid composition or concentrations. Concentrations are low in each techniques, most likely because of their quick half-life in soil.
The addition of urea did change the composition of amino acids in natural soil however not in standard soil. The addition of alfalfa or compost didn’t alter the composition or focus.
Natural gardening strategies don’t appear to considerably alter the amino acids in soil.
Water-Soluble Amino Acid Fertilizer
A brand new kind of fertilizer referred to as water-soluble amino acid fertilizer is being examined in agriculture. I’ve not seen it on the market within the gardening group, though many natural fertilizers include amino acids. It’s a concentrated powder of amino acids that’s water soluble. It may even be added to common soluble fertilizer.
Making use of this to vegetation has proven improved development in tomatoes and peppers. What will not be clear from these research is whether or not an equal quantity of nitrogen from different sources would have been simply as helpful.
Can Crops Use Proteins?
Proteins are massive molecules made up of amino acids. Within the soil of pure ecosystems, nitrogen happens predominantly as proteins, which aren’t instantly obtainable to vegetation. Crops can, nevertheless, get proteins by way of their affiliation with mycorrhizal fungi.
Current analysis reveals that vegetation have one other means of accessing the nitrogen in proteins. Roots exude enzymes that digest protein into amino acids on the floor of the foundation. Roots can then soak up the amino acids.
There may be additionally some proof that roots can suck in massive molecules by way of endocytosis.
Protein alone doesn’t assist plant development to the identical extent as inorganic nitrogen sources; nevertheless, it could actually play an essential position when each sources of nitrogen are current.
Is Urea a Good Fertilizer for Crops?
I began engaged on this publish to get a greater understanding of a plant’s capability to make use of completely different types of nitrogen. Particularly, is the urea present in fertilizers pretty much as good as nitrate?
Since urea is transformed to ammonium rapidly and vegetation can use ammonium, it must be wonderful for rising vegetation. That is very true if you happen to fertilize with every watering, as I extremely advocate.
If you happen to solely fertilize each month or two, the poor vegetation should wait a number of extra days for the urea to be transformed earlier than they get a superb dose of nitrogen.
Urea fertilizer must also be began sooner in case you are rising seedlings in new potting media. Recent media could not have the microbes wanted to transform urea, so it’d take fairly a number of additional days earlier than nitrogen is available.
Natural vs Artificial Fertilizer
My second query pertains to claims that natural sources of nitrogen, particularly amino acids and proteins, are higher than artificial sources.
Natural fertilizer can be utilized as a nitrogen supply, however it appears that evidently inorganic sources of nitrogen are simpler for vegetation. Proteins have to first be transformed to amino acids or inorganic nitrogen earlier than a lot of it may be used. That is accomplished largely by microbes, however we now know vegetation may play a task on this.
Amino acids have proven some promise as a fertilizer, however there appear to be few research that examine equal quantities of nitrogen from each artificial and natural sources. To date, they appear to be used largely as a complement to conventional inorganic fertilizer.
The actual worth of natural fertilizer nonetheless appears to be in its capability to activate the microbe group, to not feed vegetation instantly. The microbes then produce the inorganic nitrogen that vegetation use.